Machine Learning Classroom
Restructuring the Classroom Model to Accommodate for All Learning Styles
Overview
An interaction design project in which I conducted secondary research on Machine Learning trends and use cases, as well as primary research with stakeholders such as teachers and parents. The solution was a tablet-hosted Machine Learning system that employs passive inputs (eye-tracking) and manual inputs to measure and reflect learning style.
My primary roles: Research, Storytelling
Project Duration: 5 weeks (November -December 2017)
Team: Lan Vu, Nirawit Jittipairoj
Deliverable: Video prototype, presentation, specification document.
What if we could individualize lessons for different learning styles and paces, while also reducing workload for teachers?
Our solution
A system that trains itself to individual students unique needs, while improving upon the grading and curriculum model. We introduce a new way of measuring understanding, followed by automated reporting to the teacher. Teachers can spend their time with students directly, instead of with their work.
Edited by Nirawit Jittipairoj
Secondary Research on Machine Learning
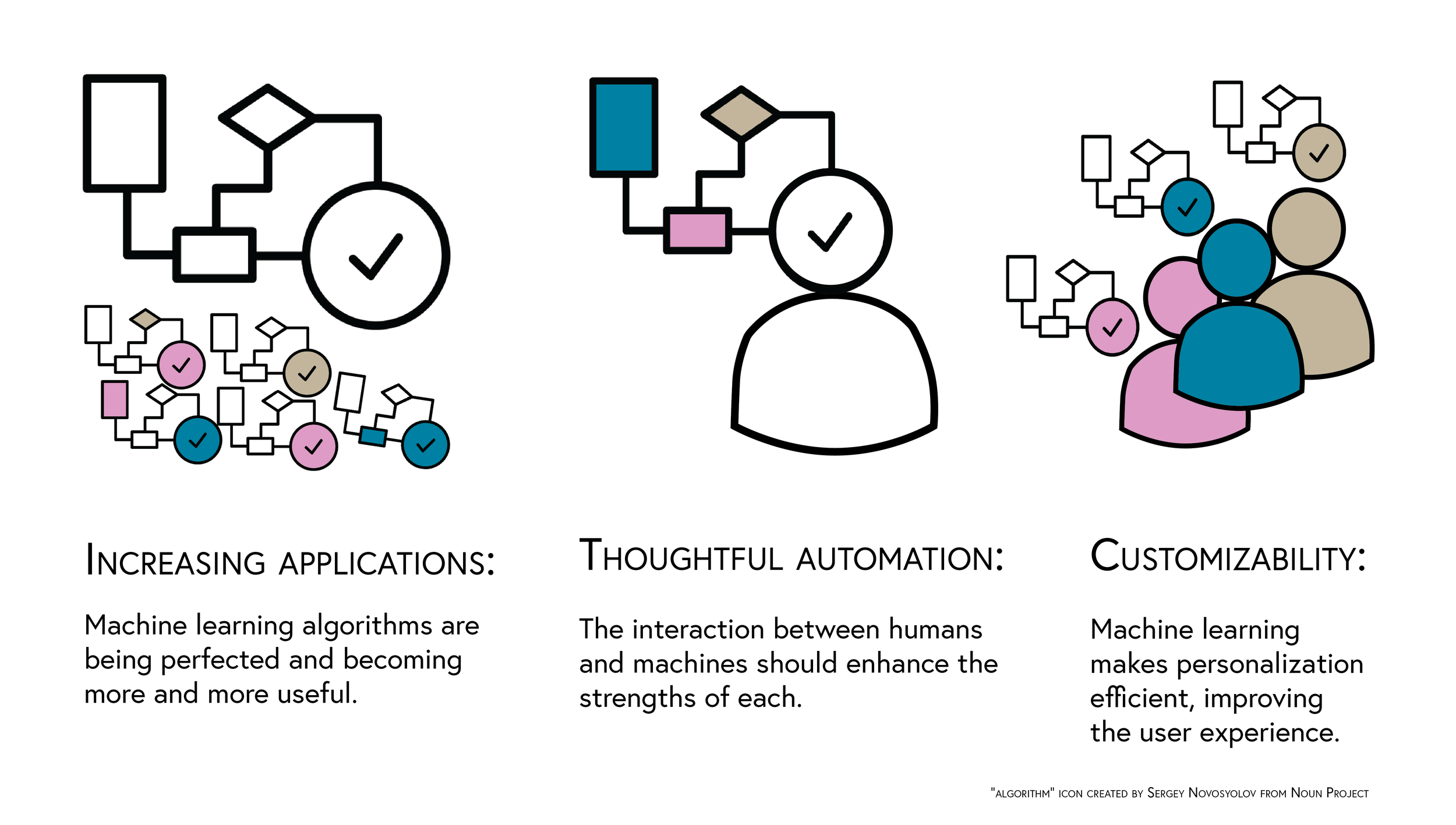
I researched the current state of machine learning by reading articles online and attending talks, and identified points to shape research and design:
Customizability could be indispensible in a learning setting, where each child has a unique way of processing information. The one-size-fits-all approach that makes of the majority of classrooms in America is an outdated system.
However, despite automation, custom lesson plans may not be possible within the rigid structure of traditional schools. Furthermore, technology in classrooms was often cited as more of a distraction than a tool. Online resources were vague about specific curriculum and technology requirements, so I decided to conduct primary research.
Primary Research
I conducted a semi-structured interview with a high school Physics teacher.
Questions
Illustration by Eliza Newman-Saul
How much freedom do teachers have with lesson planning?
What are the main challenges for students and teachers?
What are your daily tasks?
How does technology fit into the classroom?
What is the relationship between teachers and students?
"I notice if students are doing better. It's part of the job."
Would automatic grading obscure their work? "It would, but nothing would stop me from going in and looking at their work. It would still be useful, I wouldn’t have to look at all 90 of my students work. I could just look at uncharacteristically good or bad work."
Insights
01. Grading is the the most labor intensive and least satisfying task.
02. Teachers are not opposed to technology.
03. Teacher-Student relationships are the most important and most rewarding part of the job
04. Curriculum structure can vary in flexibility per subject
Design Principles
01. Foster relationships
02. Alleviate grading for teachers
03. Do not create an isolating experience
Problem Space
To identify potential intervention points throughout the school day, I storyboarded the teacher's scenario.
Storyboarding
We exchanged storyboards within our team and noted touch points.
Identifying the Roles of Teachers
We listed out the roles of teachers in two categories:
01. The formal roles required to educate,
02. and the less academic social demands.
I then marked each if they would be better filled by a human (*) or by a machine ([]). Some roles such as "keeping parents in the loop" could be completed by both.
Icon by Sergey Novosyolov, The Noun Project
Icon by Icon Fair, The Noun Project
Teaching the System: Inputs
Eye-tracking
Eye movements are indicative of concentration (Hafed and Clark, 2002; Mathot et. al, 2013), and tablet-mounted eye-trackers such as UMoove are currently on the market. Measurements of concentration would inform the system when a student might need a break. Furthermore, eye data indicates what kind of learner a student might be. For example, a student that spends time reading is probably a textual learner, while a student who looks at the picture more may be visual.
Interactions
Other inputs would be responses on review questions, time information, and calls for assistance.
Teaching the Students: Outputs
Variable Lessons
The system learns a child's learning style and outputs the appropriate medium. Lessons are pulled from a database and adjust the presentation of information based on each student. Lessons could include images, text, video, activities, audio, or crafts.
Review Questions
Questions appear as the student completes lessons. This is meant to measure comprehension and replace quizzes and homework, where feedback in the form of grades is given days after completion.
Group Activities
Students are prompted several times throughout the day to join other students for group work. Students are grouped based on differing ability to encourage teaching and learning.
Wireframes
I wireframed the teacher-facing view of the app. Essential components included a notification system, pages for each student that included learning style information, and the ability to view a students screen ("real-time toggle").
Future Directions
Rapidly increasing abilities of Machine Learning, as well as advancing portable eye-tracking technology, will make this vision much less speculative in the coming years. Coupling this with the technology initiatives of schools could impact not only education, but the larger scale of the society those children will join.